Wearable Healthcare Devices Market
Wearable Healthcare Devices Market Share & Trends Analysis Report, By Product Type (Diagnostic Devices, Therapeutic Devices, Fitness Trackers/Activity Monitors, Smartwatches, Smart Clothing and Hearables), Diagnostics), By Grade Type (Consumer-grade, Clinical-grade), By Application (General Health and Fitness, Remote Patient Monitoring, Home Healthcare, Sports and Fitness), By Distribution Channel (Online channels (e-commerce), pharmacies, hypermarkets, and specialty stores. Industry Analysis Report, Regional Outlook, Growth Potential, Price Trends, Competitive Market Share & Forecast, 2025–2033.

Historical Period: 2019-2024
Forecast Period: 2025-2033
Report Code :
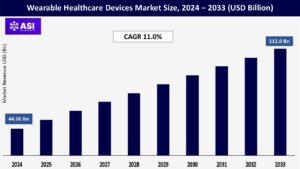
CAGR: 11.0%
Last Updated : December 25, 2025
The worldwide market for Wearable Healthcare Devices Market size was valued at approximately USD 44.06 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 112.0 billion by 2033, demonstrating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.0% during the forecast period of 2025–2033.
The wearable healthcare devices market is growing rapidly and is set to expand steadily from 2024 through 2033. As technology advances, we can expect these devices to become even smaller, smarter, and longer-lasting, with better battery life and seamless integration with existing healthcare systems. The industry is increasingly focusing on delivering personalized, proactive, and preventive care, empowering people to monitor their health more effectively and take action before problems escalate.
More and more people are taking charge of their health in a proactive way, using wearable devices to track their fitness, activity levels, sleep, and vital signs. This helps them maintain healthier lifestyles and catch potential health issues early. At the same time, awareness campaigns, social media, and health influencers are spreading the word about the benefits of self-monitoring, encouraging even more people to adopt wearables for better insight into their overall well-being.
As chronic conditions like diabetes, heart disease, hypertension, and obesity become more common worldwide, there’s a growing need for continuous health monitoring and management. Wearable devices help meet this need by providing real-time data on vital signs such as blood glucose, heart rate, and blood pressure, making it easier for both patients and healthcare providers to track health consistently. These devices can also help catch early warning signs by detecting changes or patterns that suggest complications may be developing, enabling timely intervention. In particular, the rising global number of people with diabetes is driving demand for continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices, which offer effective, real-time blood sugar tracking to support better management of the condition.
Wearable devices gather very personal health information from vital signs and activity patterns to sleep data and specific medical conditions which makes protecting this data critically important. If such sensitive information is compromised, it can result in serious privacy breaches, identity theft, or even discrimination. Because this data is often transmitted wirelessly and stored in the cloud, it’s also vulnerable to cyberattacks and unauthorized access.
Another concern is that users don’t always have a clear picture of how their data is being collected, stored, shared, or even sold, thanks to confusing privacy policies and tricky design choices that make true consent difficult. There’s growing worry about this data being shared with insurers, advertisers, or data brokers without users’ explicit knowledge or control, opening the door to potentially discriminatory practices.
While wearable devices are becoming more popular for health tracking, there are important differences between consumer-grade wearables and clinical-grade medical devices. Consumer wearables don’t always meet the same strict regulatory standards, which raises concerns about the accuracy and reliability of the data they produce, especially when it comes to diagnosing or treating medical conditions.
Sensor limitations, like motion artifacts, incorrect placement, or interference from the environment, can also lead to inaccurate readings. Many of these devices haven’t undergone rigorous clinical validation, making healthcare professionals cautious about relying on them for critical decisions, since inconsistent or incorrect data could lead to misdiagnosis or inappropriate treatment. Additionally, user errors, like incorrect manual data entry or improper usage, can further compromise the quality of the information collected.
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Segmentations | |
| By Product Type |
Diagnostic Devices Therapeutic Devices Fitness Trackers/Activity Monitors Smartwatches Smart Clothing and Hearables |
| By Grade Type |
Consumer-grade Clinical-grade |
| By Application |
General Health and Fitness Remote Patient Monitoring Home Healthcare Sports and Fitness |
| By Distribution Channel |
Online channels (e-commerce) Pharmacies HypermarketsSpecialty stores Specialty stores |
| Key Players |
Medtronic Withings Acticheck Ltd Garmin Ltd Fitbit (Google) Apple Inc. Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd Polar Electro Biotronik SE & Co. KG OMRON Healthcare Abbott Dexcom, Inc. Insulet Corporation AliveCor, Inc. Koninklijke Philips N.V. GE HealthCare |
| Geographies Covered | |
| North America |
U.S. |
| Europe |
U.K. |
| Asia Pacific |
China |
| Middle East & Africa |
Saudi Arabia |
| Latin America |
Brazil |
The Wearable Healthcare Devices Market is categorized by product type, by grade type, by application and by distribution channel. Each segment is rapidly evolving, with different areas of the industry growing at their own pace and shifting in how much of the market they represent. Each segment provide a comprehensive understanding of its dynamics and growth opportunities. The wearable healthcare devices market is a complex and dynamic landscape, and its segmentation allows for a granular understanding of its various facets, identifying key growth areas, dominant sub-segments, and regional trends.
Wearable healthcare devices can be broadly categorized based on their core function and form factor. Diagnostic and monitoring devices make up the largest share of the market, thanks to rising demand for continuous health tracking and early disease detection. These include vital sign monitors like heart rate sensors and ECG devices integrated into smartwatches and fitness trackers, wearable blood pressure cuffs, pulse oximeters for blood oxygen levels, and spirometers for lung function.
Activity monitors and fitness trackers keep tabs on steps, calories, and movement, while sleep monitoring devices track sleep stages and disturbances. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs)—which use patch-based or implanted sensors to deliver real-time blood sugar readings are a particularly fast-growing sub-segment. Other devices include neuromonitoring tools like EEGs and EMGs, fetal and obstetric monitors for pregnancy care, and simple diagnostic patches for temperature tracking.
On the other hand, therapeutic devices, though currently a smaller market segment, are growing quickly due to innovations in wearable drug delivery and rehabilitation technology. These include neurostimulation devices for chronic pain management, wearable insulin pumps for automated delivery, rehabilitation wearables with sensors to support physical therapy, and respiratory therapy devices for conditions like sleep apnea and COPD.
Wearables also vary widely in form factor. Smartwatches are the most popular type, offering a combination of health monitoring (heart rate, ECG, SpO2), fitness tracking, and smart features in an easy-to-use, connected package. Wristbands or fitness bands focus mainly on fitness and basic health metrics. Patch-based devices, which stick directly to the skin, provide discreet continuous monitoring of things like glucose or ECG and are becoming a rapidly growing niche. Hearables, or in-ear devices, can track heart rate and temperature, while smart clothing with embedded sensors monitors vital signs, posture, and activity, though adoption is still limited by challenges like comfort and washability. Shoe sensors add another layer of functionality, helping analyze gait, track activity, and detect falls.
Wearable medical devices can also be distinguished by their level of regulatory approval and intended use. Consumer-grade wearables, which make up the largest share of the market, are typically not regulated as medical devices. They’re designed for the general public and focus on wellness, fitness tracking, and providing personal health insights. These devices are widely accessible, more affordable, and easy to use examples include most fitness trackers and smartwatches you see on the market today.
In contrast, clinical-grade wearable medical devices are regulated by health authorities like the FDA in the US, meaning they meet stricter standards for accuracy, reliability, and validation. These devices are often prescribed by healthcare professionals and used in clinical settings or for remote patient monitoring of specific medical conditions. While this segment is currently smaller, it’s growing quickly as regulations become clearer and healthcare systems increasingly adopt these devices into clinical workflows.
Wearable healthcare devices can also be grouped by their primary use cases. General health and fitness is the largest segment, driven by people’s growing focus on proactive health management, wellness, and self-improvement. These devices help users track activity, monitor sleep, count calories, and generally support a healthier lifestyle.
Home healthcare is another important and growing segment, fueled by an aging population, rising rates of chronic diseases, and the push for more convenient, cost-effective care outside of hospitals. Wearables in this space enable patients to be continuously monitored from the comfort of their own homes.
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) is the fastest-growing application, gaining momentum especially after the COVID-19 pandemic. These wearables allow healthcare providers to remotely track patients with chronic conditions, monitor post-operative recovery, or care for those in rural areas helping improve outcomes and reduce hospital readmissions.
Sports and fitness is also a strong revenue-generating segment, with athletes and fitness enthusiasts using wearables to track performance, fine-tune workouts, monitor recovery, and help prevent injuries. Finally, there’s disease management, where wearables play a crucial role in monitoring conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and obesity—providing continuous data that enables more personalized, effective care.
Wearable healthcare devices reach consumers through a variety of channels. Online channels are both the dominant and fastest-growing segment, thanks to the convenience of e-commerce platforms that offer a wide selection, competitive pricing, detailed product information, and user reviews all of which make shopping easier and more informed. Pharmacies also play an important role, particularly for diagnostic and monitoring devices that may be recommended by healthcare professionals or used for self-monitoring.
Hypermarkets and retail stores give consumers the chance to see and handle devices in person before buying, which can build confidence in the purchase. Specialty stores, such as those focused on electronics or sporting goods, provide targeted selections for specific needs. Lastly, direct-to-consumer (DTC) sales are growing as manufacturers increasingly sell directly through their own websites, giving them more control over branding and customer experience.
The wearable healthcare devices market shows clear regional differences in size and growth. North America currently leads the market, thanks to its advanced healthcare system and high rates of technology adoption. Meanwhile, Asia-Pacific is expected to drive much of the future growth, fueled by its large population, rising healthcare spending, and growing awareness of health and wellness. Europe also maintains a strong position, supported by well-developed infrastructure and a strong push toward digital health Solutions. Emerging markets like Latin America and the Middle East and Africa (MEA) offer significant untapped potential, but to fully capitalize on these opportunities, challenges such as cost barriers, infrastructure gaps, and regulatory complexities will need to be addressed.
North America consistently accounts for the largest share of the global wearable healthcare devices market, estimated to be around 32–46% in 2024, with the U.S. leading the way. This dominance is supported by several key factors. The region’s advanced and well-funded healthcare infrastructure makes it easier to adopt and integrate new technologies. Higher disposable income means consumers can afford advanced, and often pricey wearable devices. There’s also strong public awareness and a cultural focus on preventive healthcare, fitness, and managing chronic diseases.
Favorable reimbursement policies, particularly for remote patient monitoring (RPM), further encourage both healthcare providers and patients to adopt wearables, a trend that’s grown even stronger with the rise of telehealth. Technological innovation is another major driver, with big players like Apple, Fitbit, and Samsung continually launching new, cutting-edge devices and investing heavily in R&D. Additionally, the high prevalence of chronic diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular conditions increases the demand for continuous health monitoring.
In terms of trends, consumer-grade wearables like fitness bands and smartwatches hold the largest market share, thanks to their popularity for personal health tracking. But the therapeutic device segment is expected to grow fastest, driven by innovations like advanced wearable pain relievers, insulin management systems, and smart asthma devices. Home healthcare continues to be a major application area. Despite this strong position, challenges remain, including the high costs of advanced devices and limited reimbursement options for certain categories, which can be barriers for uninsured or underinsured populations.
Europe holds a significant share of the global wearable healthcare devices market, about 29.8% in 2021, with projections suggesting it could reach over USD 100 billion by 2033. Several factors drive this strong position. Like North America, Europe has an aging population and a high burden of chronic diseases, which increases the demand for continuous monitoring and home healthcare solutions. The region’s well-developed healthcare systems also support the integration of digital health technologies into routine patient care.
Telehealth and remote patient monitoring have seen accelerated adoption, especially in the wake of COVID-19, highlighting the need for contactless monitoring and stronger digital engagement with patients. Regulatory innovation is another driver, with countries like Germany introducing frameworks such as DiGA that allow digital health applications, including those using wearable data, to be reimbursed, encouraging clinical adoption. In terms of trends, remote patient monitoring is one of the fastest-growing use cases. Therapeutic wearables for pain management, insulin delivery, and rehabilitation are also expanding quickly. Strap, clip, and bracelet-style devices continue to be the dominant form factors.
Countries like Germany, the UK, and the Scandinavian nations are leading the way in rolling out these technologies. However, there are challenges. The EU Medical Device Regulation (EU MDR) is very strict, requiring robust clinical evidence and ongoing post-market surveillance. While this ensures safety and effectiveness, it can also increase development costs and slow time-to-market, posing particular challenges for smaller companies and startups.
While Asia-Pacific currently holds a smaller share of the global wearable healthcare devices market than North America (about 22% of revenue in 2023), it’s expected to be the fastest-growing region over the next decade, with impressive projected growth rates ranging from 16.5% to 28.4% through 2032 or 2033. Several factors are fueling this surge. Healthcare spending is on the rise, with both governments and private sectors investing heavily to improve infrastructure and adopt modern medical technologies.
The region is home to large and rapidly aging populations, especially in countries like China, India, and Japan, leading to a higher prevalence of chronic diseases and greater demand for continuous monitoring and home-based care. There’s also growing health awareness, particularly among the expanding middle class, with more people prioritizing preventive healthcare and fitness. Technological progress, widespread smartphone use, and increasing digital literacy are making it easier for people to adopt smart wearables. Many governments in the region are also actively supporting digital health initiatives and policies that encourage the use of medical devices.
Additionally, wearables provide a cost-effective alternative to frequent hospital visits, making them especially appealing in developing economies. In terms of trends, diagnostic devices currently make up the largest share, with strong growth seen in areas like neuromonitoring and vital sign monitoring. Therapeutic devices, such as those for insulin management, are also expanding rapidly. Key markets driving regional growth include Japan, China, and India. However, the region does face challenges, such as varying regulatory requirements, diverse healthcare systems, and affordability concerns across different income groups, which can complicate adoption.
The Middle East and Africa (MEA) region represents an emerging market for wearable healthcare devices, with strong growth potential. It’s projected to reach around USD 3.29 billion by 2033, growing at a healthy CAGR of 18.1%. Several factors are driving this expansion. There’s a rising awareness of fitness and wellness, mirroring trends in other parts of the world, as more people focus on maintaining healthier lifestyles. At the same time, the growing burden of chronic diseases like diabetes and cardiovascular conditions is creating demand for continuous monitoring solutions.
Technological advancements in sensor technology, wireless communication, and AI/ML are also enabling better, smarter wearable devices. Investments in healthcare infrastructure and digital health initiatives are helping lay the groundwork for wider adoption, while an aging population is boosting demand for devices that can help manage age-related health conditions. In terms of trends, there’s strong demand for continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and wearable ECG monitors, with a focus on delivering patient-centric solutions that are both comfortable and customizable.
Saudi Arabia stands out as a key market in the region, driven by growing interest in remote patient monitoring. However, there are challenges to navigate. The MEA region has a complex and varied regulatory landscape that can make market entry time-consuming. Additionally, the affordability of high-cost wearable devices and the need to expand insurance coverage will be critical to ensuring these technologies reach more people.
The wearable healthcare devices market was valued at USD 44.06 billion in 2024.
The wearable healthcare devices market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 11.0% from 2025 to 2033.
Diagnostic and patient monitoring Segment holds the largest market share.
Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate.
Major players include Apple, Fitbit (now owned by Google), Samsung, Garmin, Medtronic, and Philips.
1.1 Summary
1.2 Research methodology
2.1 Research Objectives
2.2 Market Definition
2.3 Limitations & Assumptions
2.4 Market Scope & Segmentation
2.5 Currency & Pricing Considered
3.1 Drivers
3.2 Geopolitical Impact
3.3 Human Factors
3.4 Technology Factors
4.1 Porters Five Forces Analysis
4.2 Value Chain Analysis
4.3 Average Pricing Analysis
4.4 M & A, Agreements & Collaboration Analysis
5.1 Wearable Healthcare Devices Market, By Product Type
5.1.1 Introduction
5.1.2 Market Size & Forecast
5.2 Wearable Healthcare Devices Market, By Grade Type
5.3 Wearable Healthcare Devices Market, By Application
5.4 Wearable Healthcare Devices Market, By Distribution Channel
6.1 North America, Wearable Healthcare Devices Market, By Country
6.1.1 Wearable Healthcare Devices Market, By Product Type
6.1.2 Wearable Healthcare Devices Market, By Grade Type
6.1.3 Wearable Healthcare Devices Market, By Application
6.1.4 Wearable Healthcare Devices Market, By Distribution Channel
6.2 U.S.
6.2.1 Wearable Healthcare Devices Market, By Product Type
6.2.2 Wearable Healthcare Devices Market, By Grade Type
6.2.3 Wearable Healthcare Devices Market, By Application
6.2.4 Wearable Healthcare Devices Market, By Distribution Channel
6.3 Canada
7.1 U.K.
7.2 Germany
7.3 France
7.4 Spain
7.5 Italy
7.6 Russia
7.7 Nordic
7.8 Benelux
7.9 The Rest of Europe
8.1 China
8.2 South Korea
8.3 Japan
8.4 India
8.5 Australia
8.6 Taiwan
8.7 South East Asia
8.8 The Rest of Asia-Pacific
9.1 UAE
9.2 Turkey
9.3 Saudi Arabia
9.4 South Africa
9.5 Egypt
9.6 Nigeria
9.7 Rest of MEA
10.1 Brazil
10.2 Mexico
10.3 Argentina
10.4 Chile
10.5 Colombia
10.6 Rest of Latin America
11.1 Global Market Share (%) By Players
11.2 Market Ranking By Revenue for Players
11.3 Competitive Dashboard
11.4 Product Mapping